All About Porcelain
What is Porcelain?
Porcelain is a type of ceramic material made by heating materials, generally including kaolin, in a kiln to temperatures between 1,200 and 1,400 °C. It is known for its strength, durability, and translucent quality.
Manufacturing Process
Production of porcelain involves a series of procedures that are essential in achieving the final product. Below is a summary of porcelain production:
- Preparation of Materials: Kaolin, feldspar, and quartz make up the raw material that is used and processed and blended with other essentials.
- Shaping: The to-be-shaped formed mixture is formed to shape through various processes such as casting, pressing, or extrusion.
- Drying: Drying of pieces to evaporate moisture to avoid cracking during firing.
- Firing: The dried-out fragments are then fired at 1,200 to 1,400 °C in a furnace, which makes the material vitrify and gives it its strength and translucency.
- Glazing: It is possible to apply a glaze to the surface after the first firing, and the piece refired again in an effort to create a glossy finish.
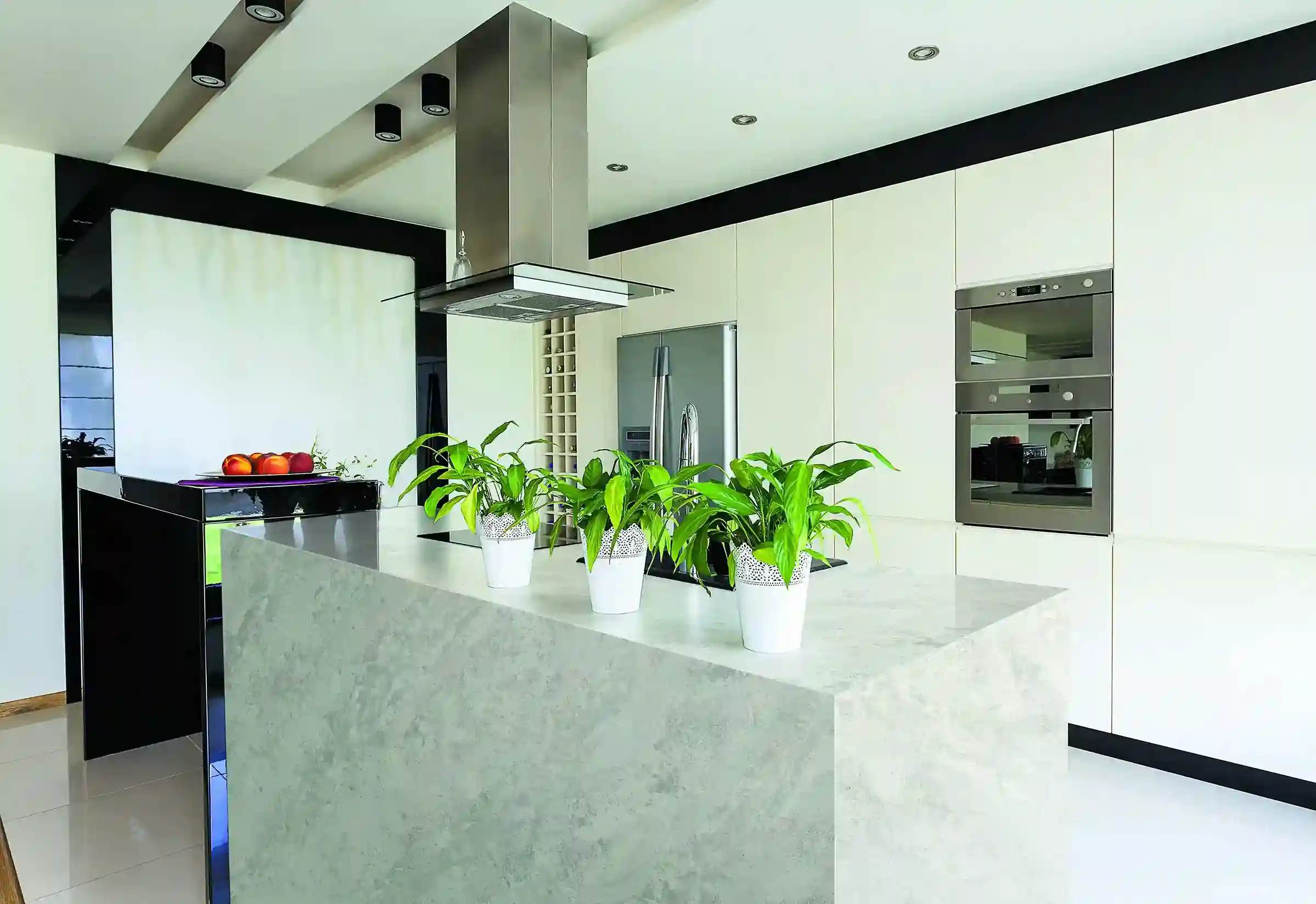

Pros and Cons of Porcelain
Pros
- Extremely resistant to wear and tear.
- Non-porous, so it's resistant to stains and water.
- Available in a broad selection of colors and designs.
- Resistant to heat, ideal for many applications.
- Low maintenance and easy cleaning.
Cons
- More costly than some other materials.
- Professional installation may be needed.
- Heavy compared to other countertop options.
- May chip or crack if hit hard.
How to Care for Porcelain
Although porcelain requires very little upkeep, it will look nicer and last longer if properly maintained:
- Cleaning: Use a gentle cloth and a mild dish soap and water to clean every day. Steer clear of abrasive cleaners and sponges.
- Stain Removal: Use a solution of baking soda and water to remove stubborn stains. Chemicals that can harm the surface should not be used.
- Heat Protection: To avoid thermal shock, warm pots and pans should always be placed on heat mats or trivets.
- Prevent Scratches: To prevent scratches, chop food on cutting boards.
- Avoid Heavy Impact: Porcelain, despite its strength, is susceptible to chipping or breaking if it is struck suddenly, so exercise caution.